Oily Skin and Enlarged Pores
Oily Skin and Enlarged Pores
Oily Skin and Enlarged Pores
Condition
Respond to congested, oily skin and enlarged pores with our range of pore-refining treatments here at The R Clinic.
What is Oily Skin and Enlarged Pores?
What is Oily Skin and Enlarged Pores?
Your body naturally releases sebum (natural skin oils) made by the sebaceous gland. Sebum is released through your pores to keep your skin protected and hydrated. Sebum is made up of precious skin oils, lipids, which are primarily natural squalene, waxes and oils.
When our sebaceous glands work overtime and produce excess sebum this can lead to excess oil on our skin and inside our pores resulting in oily, shiny skin with visibly enlarged pores.
What causes Oily Sin and Enlarged Pores?
What causes Oily Sin and Enlarged Pores?
Oily skin and enlarged pores occur when your sebaceous glands, triggered by factors such as environmental conditions, hormonal imbalances, or diet, gets knocked out of balance, producing more oil than your skin needs. Using certain over the counter products such as cleanser for oily skin can also damage our skin’s magic natural barrier causing an increase of oil. This causes pores to expand with trapped dead skin and excess oil, making them appear large and unsightly.
How can we help?
How can we help?
With an in-depth knowledge of skin, skin conditions and pharmaceuticals, our doctor led team have the expertise to guide your treatment for oily skin by taking a holistic approach to get balance back to your skin. At the R Clinic we have both cosmeceutical topical treatments and medi-aesthetic treatments to put a stop to your oily skin. Return balance to your skin by repairing its natural barrier through micro-needling, LED therapy, and chemical peels. Continue treatment at home with our range of tailored UniverSkin cosmeceutical range.
FAQ
Have further questions or want to learn more?
What is sebum?
Sebum is a complex and variable mixture of lipids including:
- Glycerides
- Free fatty acids
- Wax esters
- Squalene
- Cholesterol esters
- Cholesterol
Sebum is produced by sebaceous glands when they disintegrate. The gland cells last about a week, from formation to discharge. The sebaceous glands produce lipids, triglycerides, which are broken down by bacterial enzymes (lipases) in the sebaceous duct to form smaller compounds, free fatty acids. The oil on the surface of skin is a complex mixture of sebum, lipids (from the surface skin cells), sweat and environmental material.
What does sebum normally do?
Sebum has the following functions:
- It reduces water loss from the skin surface
- It protects the skin from infection by bacteria and fungi
- It contributes to body odour
- It is colonised by the bacteria Proprionibacterium acnes, which may have a role in immune system regulation
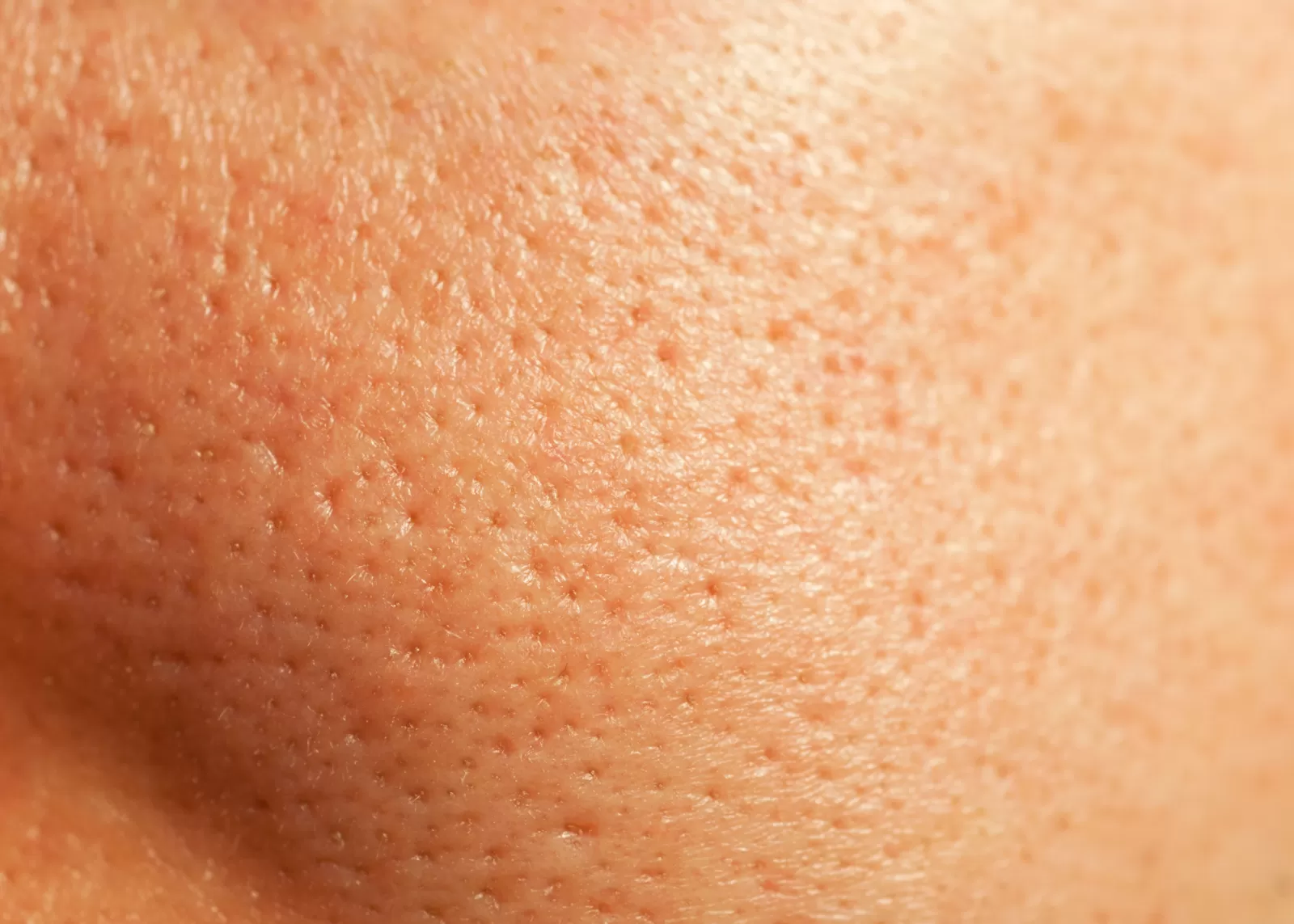
What Are Pores?
Pores are where we house our natural oils, which are also known as sebum.
They’re also connected to our hair follicles and are a normal part of our skin.
Getting rid of pores completely is physiologically impossible, but there are ways to look after our skin to help minimise their appearance if enlarged pores are an issue for you.
What causes large open pores?
There are several causes of large-looking open pores. They include:
- high levels of oil (sebum) production
- reduced elasticity around pores
- thick hair follicles
- genetics or heredity
- reduction of collagen production in skin, caused by aging
- sun damage or overexposure to the sun
How does our hormone regulate sebum production?
Sebum production is under the control of sex hormones (androgens). The most active androgens are testosterone, 5-testosterone (DHT) and 5-androstene-317diol. These hormones and others are made by the sex glands (ovary in females, testis in males) and by the adrenal gland.
Androgens are made more active by enzymes in the skin and sexual organs. Type I 5α-reductase acts in the skin and Type II 5α-reductase acts in the sexual organs. These enzymes convert less active androgens into the active testosterone and 5-testosterone (DHT). These more active androgens stimulate sebaceous gland cells to produce more sebum.
Can dehydration cause oily skin?
Dehydrated skin is another common culprit of oily skin. If you would describe your skin as both oily and dry, then it’s chronically dehydrated. When our skin isn’t adequately hydrated (lacking water) it compensates by making more oil, instead of water. Along with an increase in oil production, dehydration slows down the skin’s natural shedding process, causing dead skin cells to get stuck within the pores – a perfect storm for blackheads and breakouts. This is why cancelling your moisturiser is a bad idea. Both external and internal hydration is critical to keeping skin healthy. If you’re an oily skin you’ll want to incorporate a lightweight, oil-free moisturiser that will feed your skin essential moisture without adding oil.